1. Hardware [Kembali]
Gambar Button
GambarLED
MASTER
#include<SPI.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDR 9
bool state, lastState;
int analogPin = 0;
int val = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(analogPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(analogPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
SPI.begin();
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV8);
}
void loop() {
state = digitalRead(analogPin);
if(state != lastState){
delay(50);
val = map(analogRead(analogPin), 0, 1023, 255, 1);
Serial.print(val);
}
}
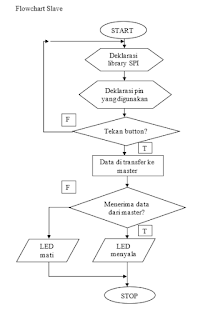
SLAVE
#include<SPI.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDR 9
int LED = 13;
int rd;
int br;
void setup() {
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
SPCR |= _BV(SPE);
SPI.attachInterrupt();
}
void loop() {
delay(50);
br = map(rd, 1, 255, 100, 2000);
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
delay(br);
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
delay(br);
}
#include<SPI.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDR 9
bool state, lastState;
int analogPin = 0;
int val = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(analogPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(analogPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
SPI.begin();
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV8);
}
void loop() {
state = digitalRead(analogPin);
if(state != lastState){
delay(50);
val = map(analogRead(analogPin), 0, 1023, 255, 1);
Serial.print(val);
}
}
SLAVE
#include<SPI.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDR 9
int LED = 13;
int rd;
int br;
void setup() {
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
SPCR |= _BV(SPE);
SPI.attachInterrupt();
}
void loop() {
delay(50);
br = map(rd, 1, 255, 100, 2000);
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
delay(br);
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
delay(br);
}
Buatlah Program menggunakan input potensiometer menggunakan komunikasi SPI
/MASTER
#include <SPI.h> //Deklarasi library SPI
void setup (void) {
Serial.begin(115200); //Set baud rate 115200
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// disable Slave Select
SPI.begin ();
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV8); //divide the clock by 8
}
void loop (void) {
char c;
digitalWrite(SS, LOW); //enable Slave Select
// send test string
for (const char * p = "Hello, world!\r" ; c = *p; p++)
{
SPI.transfer (c);
Serial.print(c);
}
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); // disable Slave Select
delay(2000);
}
//SLAVE
#include <SPI.h>
char buff [50];
volatile byte indx;
volatile boolean process;
void setup (void) {
Serial.begin (115200);
pinMode(MISO, OUTPUT); // have to send on master in so it set as output
SPCR |= _BV(SPE); // turn on SPI in slave mode
indx = 0; // buffer empty
process = false;
SPI.attachInterrupt(); // turn on interrupt
}
ISR (SPI_STC_vect) // SPI interrupt routine
{
byte c = SPDR; // read byte from SPI Data Register
if (indx < sizeof buff) {
buff [indx++] = c; // save data in the next index in the array buff
if (c == '\r') //check for the end of the word
process = true;
}
}
void loop (void) {
if (process) {
process = false; //reset the process
Serial.println (buff); //print the array on serial monitor
indx = 0; //reset button to zero
}
}
#include <SPI.h> //Deklarasi library SPI
void setup (void) {
Serial.begin(115200); //Set baud rate 115200
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// disable Slave Select
SPI.begin ();
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV8); //divide the clock by 8
}
void loop (void) {
char c;
digitalWrite(SS, LOW); //enable Slave Select
// send test string
for (const char * p = "Hello, world!\r" ; c = *p; p++)
{
SPI.transfer (c);
Serial.print(c);
}
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); // disable Slave Select
delay(2000);
}
//SLAVE
#include <SPI.h>
char buff [50];
volatile byte indx;
volatile boolean process;
void setup (void) {
Serial.begin (115200);
pinMode(MISO, OUTPUT); // have to send on master in so it set as output
SPCR |= _BV(SPE); // turn on SPI in slave mode
indx = 0; // buffer empty
process = false;
SPI.attachInterrupt(); // turn on interrupt
}
ISR (SPI_STC_vect) // SPI interrupt routine
{
byte c = SPDR; // read byte from SPI Data Register
if (indx < sizeof buff) {
buff [indx++] = c; // save data in the next index in the array buff
if (c == '\r') //check for the end of the word
process = true;
}
}
void loop (void) {
if (process) {
process = false; //reset the process
Serial.println (buff); //print the array on serial monitor
indx = 0; //reset button to zero
}
}
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) merupakan salah satu mode komunikasi serial synchrounous kecepatan tinggi yang dapat digunakan pada banyak microcontroller, termasuk Arduino. Untuk komunikasi SPI sendiri, membutuhkan paling tidak tiga jalur, yakni MOSI, MISO, dan SCK. Melalui komunikasi ini data dapat saling dikirimkan baik antar microcontroller, maupun antara microcontroller dengan peripheral lainnya yang mendukung komunikasi dengan SPI
1.




Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar